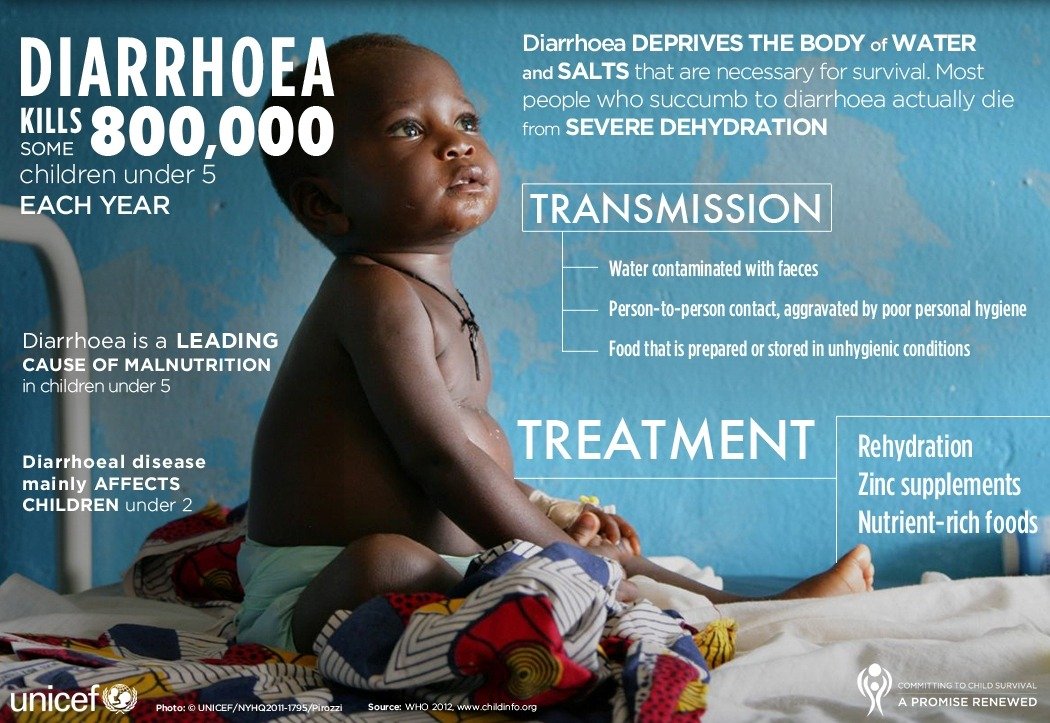
Of course, having diarrhea, or frequent defecation with watery loose stool is reasonable to get upset. It all results from an abnormal increase in bowel movements. Normally fluids are absorbed in colon leaving semisolid stools. But increased bowel movements do not permit enough time for fluid absorption. The stools may be accompanied by blood, mucus, or have an offensive odor.
Diarrhea could be a sign of food poisoning. In this case, it aids in expelling the invader/microbe to outside if there is any. Usually, no treatment is required as it ends in a few days. However, its occurrence for a long time can be due to a gut disorder such as irritation of the bowel.
Common causes
- Infection (viral, bacterial, or parasitic).
- Food which the body is allergic to.
- The extra load of food on the digestive system.
- Malabsorption of nutrients.
- Taking laxatives exaggeratedly.
- Medications.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Symptoms
- Watery loose stool.
- Abdominal pain.
- Bloating.
Other possible symptoms
- Fever.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Dietary-induced Diarrhea
The most known are lactose intolerance and gluten sensitivity. First of all, lactose is the milk sugar, thus, it’s in dairy products made from raw milk. While gluten is a protein in wheat and barley. To overcome lactose or gluten intolerance, cut off ingesting any foods containing either lactose or gluten because the nutritional value is present in various foods. Try dairy products and milk free from lactose. Big thanks to the nowadays tech of the food industry to let this come true.
Although an excess of fiber may lead to diarrhea, soluble fiber is very helpful for stopping diarrhea. The fiber, in this case, acts as a sponge that absorbs water so that the stool gets more firm.
• 10 Signs You’re Gluten Intolerant
Medication could be the Problem!
Frankly, any medication has side effects, even a little. The point is how intense are they and for how long would they last. Hence, diarrhea occurs too often as a side effect of taking a variety of medications.
- Chemotherapeutic agents (for cancer treatment).
- Some antibiotics like amoxicillin.
- NSAIDs (for analgesia, painkilling, fever, and inflammation).
N.B. Adjusting the timing and doses of any medications taken is greatly substantial.
The Risk of long Diarrhea episodes
Body dehydration is a big concern while having diarrhea, most particularly if severe. Hence, stick to the daily recommendation of drinking water which is, at least, 8 glasses of water every day. In some cases, oral rehydration therapy is a must to compensate for the loss of water and electrolytes.
You have to visit the doctor if
- Fever exceeded 39°c
- Diarrhea persisted for more than 3 days
- You have bloody or black stools
Spastic colon
A case which is known also as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) that most often has a precursor of stressful conditions. Besides, it leads to digestion problems, thereby diarrhea or constipation occurrence. Besides, there may be abdominal pain and bloat.
Traveler’s diarrhea
It’s usually mild and taking medications like bismuth subsalicylate and loperamide are enough because the first is an adsorbent, whereas the latter is an antimotility medication.
N.B. Diarrhea with unknown reasons may need a combination of sulfa medication, metronidazole, and an anti-motility medication to treat it.

Leave a Reply