Infectious diarrhea, often called gastroenteritis, is an inflammation involving both the stomach and the small intestine. Occasionally, it has a non-infectious cause but results more often from food and water contamination. Thereby, it’s more prevalent in places with low water quality and poor food hygiene. Usually, infectious diarrhea is acute, self-limited, and does not require medications.
Common symptoms of Gastroenteritis
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea.
- Stomach pain.
Other symptoms
- Headache.
- Fever.
Transmission of pathogens
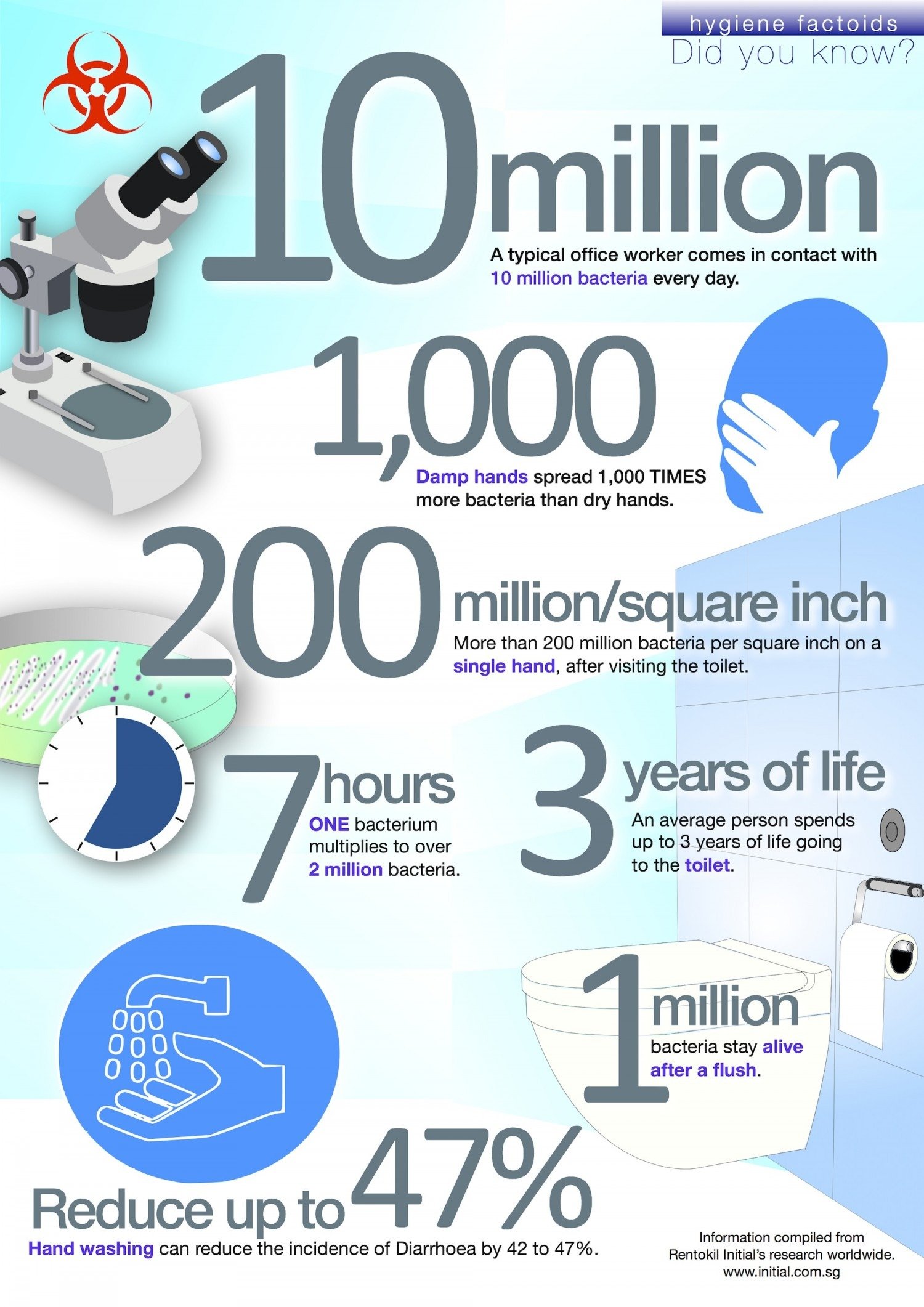
Most gastrointestinal pathogens are transmitted by fecal-oral contact, contaminated surfaces, hands, water, or food. Infected people pass the pathogen from their bodies to the environment through stool while sick.
Lack of hygiene in closed places can increase the spread of infection. Hence, the infection could be common in schools. Children can spread the infection to family members due to close contact.
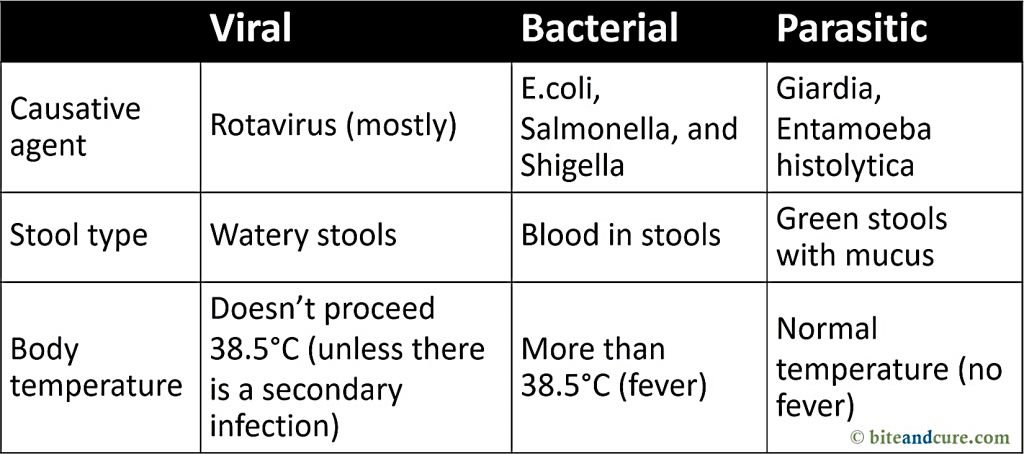
Causes of Infectious Diarrhea
Viruses are the main cause in children, but not for adults because of the acquired immunity. Instead, Campylobacter bacteria are the major cause of infectious diarrhea in adults.
• Bacterial
The top 4 species are E. coli, Campylobacter, Salmonella, and shigella. Salmonella causes also typhoid fever, whereas, shigella is one cause of dysentery.
• Parasitic
Commonly, it’s either Giardia lamblia or Entamoeba histolytica, but mostly giardia. There is mucus with the green-colored stools and no fever.
• Viral
Perhaps a viral infection in GIT is why the folks call it stomach flu or intestinal flu. Rotavirus has been reported to be the viral cause in children. While norovirus is the leading cause in adults. Besides, a secondary infection may shoot the body temperature above 38.5°C.
There is no particular medication for the treatment of viral diarrhea. The only purpose, in this case, is to rehydrate the body because dehydration can lead to serious problems. Severe dehydration may require hospitalization for treatment with intravenous fluids.
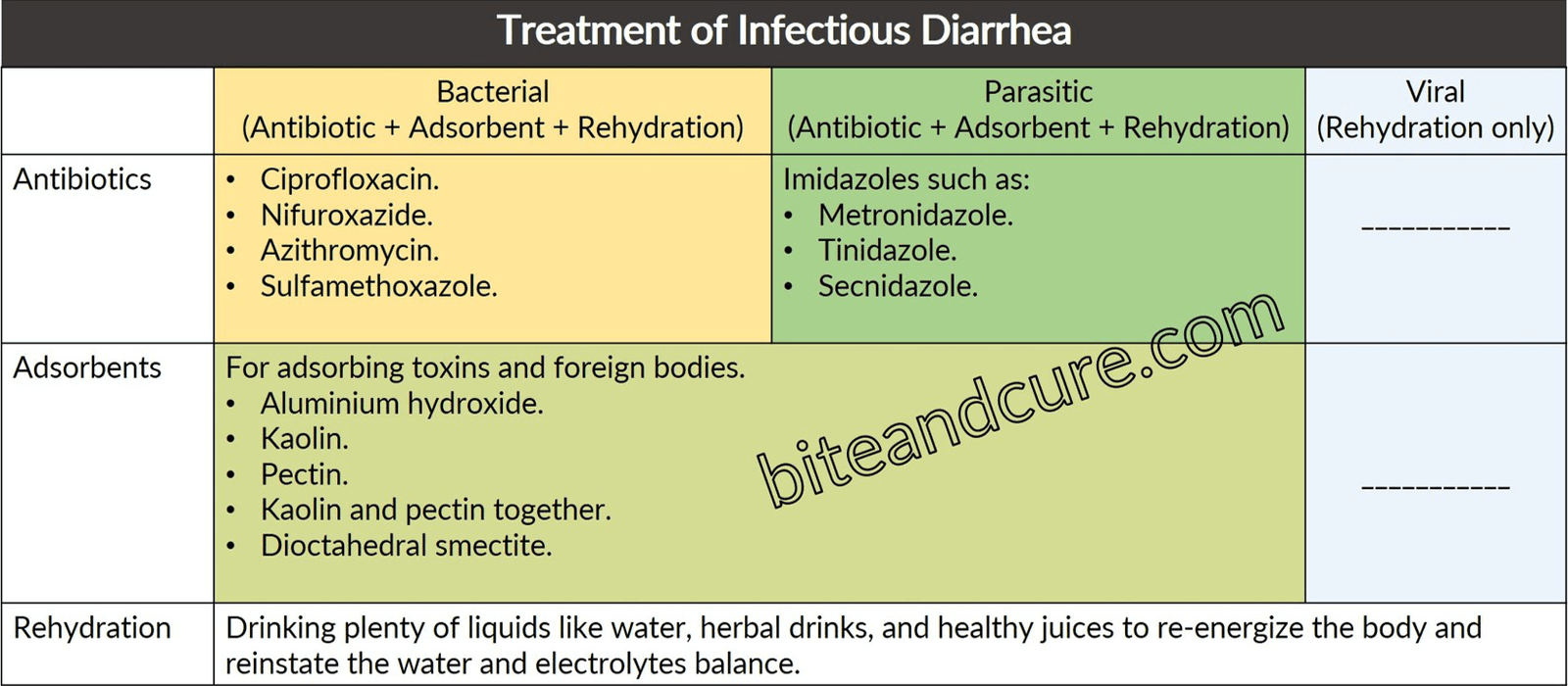
Take care
- Do not overuse antibiotics, especially for a long period.
- Anise, clove, cinnamon, and peppermint percolated drinks are effective for bloating and gas.
N.B. Do not take anti-motility medications for infectious diarrhea because they delay the elimination of pathogens, and the diarrhea may get worse.
Prevention of Infectious Diarrhea
Hygiene practices while eating, drinking, and using the toilet are important to decrease the predisposition to infection. Also, washing hands properly and avoiding unclean, undercooked, or improperly preserved foods are significant.
- Isolate the infected people from others.
- Disinfect the surrounding surfaces with effective agents.
- Strictly wash your hands before and after contact with infected persons and contaminated surfaces.
Food safety
Cook the food well to get rid of germs, mainly:
- Vegetables and fruits.
- Poultry.
- Meat.
- Seafood.
- Eggs.
- Raw sprouts.
N.B. Drink pasteurized milk and get authentic milk products only.
Hygiene rules for cookery
- Clean the surfaces with a strong detergent.
- Wash your hands well before cooking.
- Prepare raw meat, poultry, and seafood away from other foods.
- Use different knives and separate cutting boards for meat and vegetables.
- Avoid the foods getting into contact with any chemicals.
- Keep sick people away from food while it’s handled and prepared.
- Wash the cooking utensils and eating dishes with hot water.
- Wipe the table setting with a detergent.
- Store foods at the proper temperature.
Leave a Reply