The human brain is a very perplexing organ that has amazed and baffled people throughout the ages. Some scientists have devoted their entire lives to the exegesis of how the brain works. Yet, the human brain isn’t quite perceivable.
#1 At birth, the brain has an average weight of 350-400 gm, but for adults, the brain averages 1300-1400 gm. It’s composed of about 77-78% water, 10-12% lipids, 8% protein, 1% carbohydrates, 2% soluble organics, and 1% inorganic salts.
#2 The brain is encased in a hard protective skull that by the age of two is already 80% of its eventual adult size. During adolescence, all the body experiences significant changes in physical appearance. Whereas, the human brain has a little room for size expansion.
#3 The cerebral cortex (outermost tissue of cerebrum) is the largest part of the brain, forming about 85% of the brain. This part is greatly important for thinking, awareness, and attention. With 100,000 miles of blood vessels in the brain, it comprises only 2% of the human body’s average weight.
#4 There are about 100 billion neurons in the human brain, the same number of stars in our galaxy! The left hemisphere of the brain has 186 million more neurons than the right hemisphere. Although it has billions of nerve cells and trillions of synaptic connections, it only uses 20% of the body’s energy.
#5 Speaking of what it can do, the human brain is in some ways unable to match the brain functioning of lower animals. This means its capabilities are quite unrivaled.
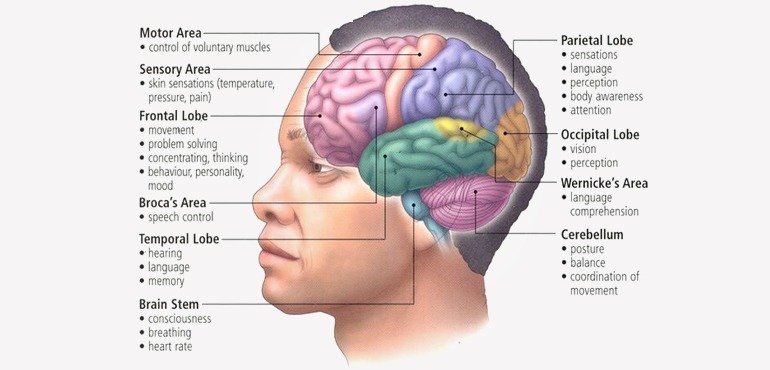
#6 The energy the brain uses is enough to light a 25-watt bulb. One of the weird facts is that a single human brain is capable of generating more electrical impulses in one day than by all the telephones in the world. The brain processes around 70,000 thoughts on an average day.
#7 Salmon, caribou and migrating birds have navigational abilities that have no parallel human abilities. Even dogs and cats have a hearing and smelling senses which are far more superior than those of humans.
#8 Studies show that brain waves are more active while dreaming than when being awake. Everyone dreams and because you don’t remember your dreams does not mean you don’t dream. Also, blind people have dreams which are more than just visual images. Whether they dream in pictures depends on either they were born blind or lost their vision later.
#9 Most people dream about 1-2 hours with an average of 4-7 dreams each night. Sometimes they forget the whole dream. In these cases five minutes after a dream, people forget half of the dream and ten minutes after a dream, they forget over 90% of it.
#10 The brain can stay alive for 4 to 6 minutes without oxygen. Afterward, the cells begin to die.
The Human Brain’s Plasticity is Outstanding
Yet, no other animal on this planet can communicate, solve problems, or even think abstractly about itself and the future as we humans do. These relative strengths and weaknesses can be due to the unique and complex structure of the human brain. Neuroscientists have traced these characteristics to the human brain’s remarkable flexibility, or what the researchers call “plasticity“.
The brain’s plasticity allows for marked capacity changes because of the usage, practice, and experience throughout one’s entire life. This idea that the human brain continues to develop and improve during a lifetime is a relatively new concept.
Brain size is no longer among the direct criteria for determining brain capacity. Even neuroscientists once believed that the basic structure and abilities of the adult brain develop early in life and do not change. Then several provocative experiments dramatically complicated such thinking.
• 36 Amazing Facts about the Human Body
A Step to Understanding the Human Brain
An experiment was done to examine various effects of an enriched environment on brain development. The enriched media used was “amusement park” for rats.
Researchers kept one group of the rats in an empty cage, devoid of any stimulus. While another group lived in a cage filled with ladders, platforms, boxes, and other toys. During the experiment, researchers used MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) technology to observe the brain development of the two groups.
Those rats in the enriched environment full of stimulus developed heavier and thicker brains. Their brains got more neurons and synaptic connections than the brains of the other group rats.
Such results were more noticeable in humans. They confirmed that life experiences and environment do not only define the brain’s particular architecture but also can continue to spark the expansion of its capacity to function.
Leave a Reply